Redux 是一款小巧的 JavaScript 状态容器,提供可预测化的状态管理。Redux 常见于 React 应用的数据状态管理,但是 Redux 不仅仅局限于 React,还支持其它 UI 库。
Redux 应用示例
在 Redux 中,应用的整体全局状态以对象树的方式存放于单个 store 中。唯一改变状态树(state tree)的方法是创建 action。action 是一个描述发生了什么的对象,并将其 dispatch 给 store。要指定状态树如何响应 action 来进行更新,可以编写纯 reducer 函数,这些函数根据旧 state 和 action 来计算新 state。
1 | import { createStore } from 'redux'; |
Redux 的应用场景
- 同一个 state 需要在多个 Component 中共享,例如应用需要登录,登录后的用户信息可以存放于 store 中
- 需要操作一些全局性的常驻 Component,比如 Notifications,Tooltips 等
- 太多 props 需要在组件树中传递,但其中大部分只是为了透传给子组件
- 业务太复杂导致 Component 文件太大,可以考虑将业务逻辑拆出来放到 Reducer 中
不适用的场景:
使用 Redux 需要创建很多模版代码,会让 state 的更新变得非常繁琐,如果应用数据流向比较简单,可以不使用 Redux 。
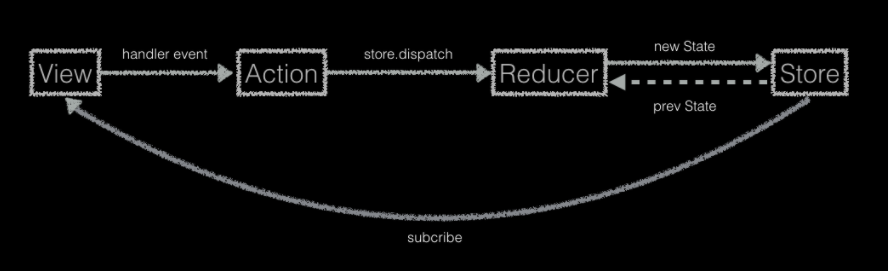
Redux 数据流向
严格的单向数据流是 Redux 架构的设计核心。Redux 应用中数据的生命周期遵循下面 4 个步骤:
- View 中的某个操作调用
store.dispatch(action)。 - Redux store 调用传入的 reducer 函数,入参为 当前的 state 和 action。
- 根 reducer 应该把多个子 reducer 输出合并成一个单一的 state 树。
- Redux store 保存了根 reducer 返回的完整 state 树。
Redux 数据流向
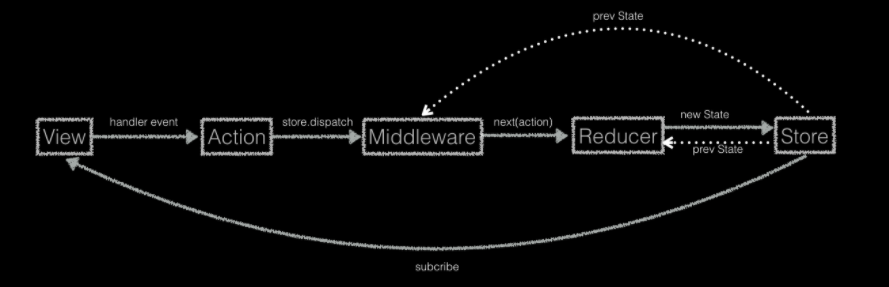
带 middleware 的 Redux 数据流向
Action: Action 是把数据从应用传到 store 的有效载荷,本质上是 JavaScript 普通对象。action 内必须使用一个字符串类型的 type 字段来表示将要执行的动作。
Reducer: Reducer 指定了应用状态的变化如何响应 action 并发送到 store 的。它是一个纯函数,接收旧的 state 和action,返回新的 state 。
State: State 记录了应用的状态。在 Redux 应用中,所有的 state 都被保存在一个单一对象中,即 store 中。
Store: Redux 应用只有一个单一的 store,它维持应用的 state,提供 getState() 方法获取 state;提供 dispatch(action) 方法更新 state;通过 subscribe(listener) 注册监听器;通过 subscribe(listener) 返回的函数注销监听器。
Redux 和 Flux 的区别
Flux
- Flux 是用于构建用户界面的应用程序架构,通过单向数据流补充 React 可组合的视图组件
- Flux 更像模式而非框架,没有任何硬依赖
- Flux 架构的应用包含 4 部分
- Action
- 通过 Action creators 创建
- 每个 Action 拥有 type 或类似属性
- 传递给 Dispatcher
- Dispatcher
- 分发 Actions 给所有注册 Store 的回调函数
- Store
- 接受 Action 更新数据后,触发 change 事件,通知 View
- 可以由多个 Store
- View 视图组件,即 Controller-View
- change 事件,从 Store 取回数据,将数据传递给子组件或更新组件状态
- 响应用户输入,生成新的 Action
- Action
Redux
- Redux 是 JavaScript 应用的可预测状态容器
- Redux 对不同框架都有完整实现,Facebook 官方推荐使用代替 Flux
- Redux 架构与 Flux 基本一致,但做了简化
- State 只读,更改 State 的方式是返回新的对象,即引入 Reducer 纯函数
- Action 与 Dispatcher ,只需返回包含 type 和 payload 属性的对象
- Store
- store 唯一
- createStore 基于 Reducer 纯函数创建
store.dispatch()调用 Action
- View
- 通过
store.getState()获取最新状态 - 通过
store.subscribe()订阅状态更新store.subscribe()返回函数可取消订阅
- 通过
综上,Redux 与 Flux 都基于单向数据流,架构相似,但 Redux 默认应用只有唯一 Store,精简掉 Dispatcher,引入 Reducer 纯函数,通过返回新对象,而不是更改对象,更新状态。
对比 Flux 的官方实现,Redux 的 API 更简洁,并且提供了如 combineReducers 等工具函数及 React-Toolkit 工具集,以及对状态的撤销、重做和持久化等更复杂的功能。提供如 React-Redux 等简化 Redux 与其他第三方库的连接。
Redux 和 Vuex 的区别
Vuex 和 Redux 的本质思想是一致的,均是将数据从视图中抽离的方案,通过单一的数据源 store 和可预测的数据变化反馈视图的改变。
- Redux 不仅仅局限于 React,还支持其它 UI 库;Vuex 和 Vue 深度绑定
- Vuex 定义了 state、getter、mutation、action 四个对象;Redux 定义了 store、reducer、action
- Vuex 事件触发方式 包括 commit 同步和 dispatch 异步;Redux 同步和异步都是用 dispatch
- Vuex 中 state 统一存放;Redux 中 store 依赖所有 reducer 的初始值
- Vuex 中有 getter 可以便捷的得到 state; React-redux 中 mapStateToProps 参数做了这个工作
- Vuex 中的 action 可以使用异步 ajax 请求;Redux 中的 action 仅支持发送数据对象,异步 ajax 需要使用 redux-thunk 或 redux-saga 等第三方 middleware
- Redux 中的是不可变数据,Vuex 中的数据是可变的。Redux 每次使用新的 store 替换旧的 store,Vuex 是直接修改 state
- Redux 在检测数据变化的时候,是要通过 diff 的方式进行比较的,而 Vuex 是通过 getter/setter 来比较的
Redux 和 MobX 的区别
- Redux 的编程范式是函数式;Mobx 是面向对象的
- Redux 中的数据是不可变对象,每次更新返回一个新的数据;MobX 中的数据从始至终都是同一份引用
- MobX 没有全局的状态树,状态分散在各个独立的 store 中;Redux 中的 store 是全局唯一的
- MobX 相对 Redux 来说会少些工程化模板
- MobX 中使用 async/await 或 flow 来处理异步逻辑;Redux 需要使用第三方 middleware
Redux 的核心原则
Redux 设计和使用遵循三个基本原则:
- 单一数据源,Store 唯一
整个应用程序的状态 State 存储在单一对象树 Object tree 中
Object tree 只存在唯一的 Store 中
单一对象树让跟踪状态的时间变化,调试和检查应用程度都更加容易 - 状态是只读的
Redux 假设开发者永远不会更改数据,而是在 Reducer 中返回新对象来更新状态
更改状态的唯一方法是发出一个动作 Action,Action 是对已发生事情的抽象描述的对象
数据变更,如用户输入和网络请求都不能直接更改状态 - Reducer 是纯函数,用来归并状态 State
接受原状态和 Action,返回新状态reducer(state, action) => new State
纯函数,无副作用,输出和输入一一对应,与执行上下文、时间、调用次数无关。不应在函数内请求 API,操作 DOM,使用Date.now()等时间耦合方法或随机值
React Context 和 Redux 的区别
ReactContext
- React Context API 是为了解决跨组件层级传递 props 的效率问题
- 试验性的 Context API 存在问题
- 提供数据源的父组件和接收数据的子组件间的某个组件的 shouldComponentUpdate 返回 false 跳过更新,子组件也会被动跳过更新
- ContextAPI 正式在 React16.3 引入,使用方法
- 创建 context 对象实例:
const MyContext = React.createContext(defaultValue)
订阅 context 的变化: 使用<MyContext.Provider value={/* 某个值 */}>组件去声明想要传递的数据源 - 消费数据
高阶组件写法<MyContext.Consumer>{vaule=> /* 基于 context 值进行渲染 */ }</Consumer>
Hook写法const value = useContext(MyContext)
- 创建 context 对象实例:
Redux
- Redux 是 JavaScript 应用的可预测状态容器
Redux 使用方法
- 声明 reducer 函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10const reducer = (state, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'INCREMENT':
return state + 1;
case 'DECREMENT':
return state - 1;
default:
return state;
}
}; - 创建 store 对象
1
2import { createStore } from 'redux';
const store = createStore(reducer); - 使用 state dispatch
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14const MyComponent = ({ value, onIncrement, onDecrement }) => (
<>
{value}
<button onClick={onIncrement}>+</button>
<button onClick={onDecrement}>-</button>
</>
);
const App = () => (
<MyComponent
value={store.getState()}
onIncrement={() => store.dispatch({ type: 'INCREMENT' })}
onDecrement={() => store.dispatch({ type: 'DECREMENT' })}
/>
);
- 声明 reducer 函数
目的
- ReactContext 解决跨组件层级传递 props 的效率问题
- Redux 是 JavaScript 应用的可预测状态容器,拥有完整的状态管理功能
- 更新机制
- ReactContext:Context 的 value 更新,它内部所有消费组件都会重新渲染,并且不受制于 shouldComponentUpdate 函数,需要手动优化
- 避免使用对象字面量作为 value
- 拆分 Context
- 记忆化
- 使用 createContext 的第二参数手动优化
- Redux
- 只有当前组件所消费的状态值改变,当前组件才会被更新
- ReactContext:Context 的 value 更新,它内部所有消费组件都会重新渲染,并且不受制于 shouldComponentUpdate 函数,需要手动优化
- 调试
- ReactContext 支持 ReactDevTools 调试
- Redux 支持 Redux DevTools 调试
- 可以方便地跟踪应用的状态何时、何处、为什么及如何改变
- Redux 架构允许开发者记录更改,使用“时间旅行调试”
- 中间件
- ReactContext 不支持中间件
- Redux 支持 applyMiddleware 将所有中间件组成一个数据,依次执行,最后执行
store.dispatch,依靠中间件扩展 Redux 功能,如简化异步操作等
React 访问 ReduxStore 的方法
- connect:适合 React 组件访问 ReduxStore
1 | import React from 'react' |
- 导出 store:适合非服务端渲染
- 创建 store 并导出
1
2
3
4import { createStore }from 'redux'
import reducer from './reducer'
conststore = createStore(reducer)
export defaultstore - 引入 sotre 通过 getState 获取状态
1
2
3
4
5import store from './store';
export function get() {
const state = store.getState();
const { value } = state;
}
- 创建 store 并导出
- 使用 redux-thunk 的第二参数 getState
1 | import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from 'redux'; |
- 手写中间件 middleware,截获 action 的 payload,或者直接输出 getState 方法
1 | import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from 'redux'; |
Redux 中异步请求数据时发送多 Action 方法
异步请求数据等异步操作通常要发出三种 Action
- 操作发起时 Action,以 start 为例
- 操作成功时 Action,以 success 为例
- 操作失败时 Action,以 failure 为例
发送多 Action 方法:
- mapDispatchToprops
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12const mapDispatchToprops = dispatch => {
return {
asyncAction() {
dispatch({ type: 'start' })
fetch('/api').then(res => res.json).then(data => {
dispatch({ type: 'success', payload: { data } })
}).catch(error=> {
dispatch({ type: 'failure', payload: { error } })
}))
}
}
} - redux-thunk,使 dispatch 支持传入函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from 'redux'
import thunk from 'redux-thunk'
import reducer from './reducer'
const store = createStore(reducer, applyMiddleware(thunk))
const asyncAction = dispatch => {
dispatch({ type: 'start' })
fetch('/api').then(res => res.json).then(data => {
dispatch({ type: 'success', payload: { data } })
}).catch(error => {
dispatch({ type: 'failure', payload: { error } })
}))
}
store.dispatch(asyncAction()) redux-promise,使 dispatch 支持传入 Promise
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from 'redux'
import promiseMiddleware from 'redux-promise'
import reducer from './reducer'
const stroe = createStore(reducer, applyMiddleware(promiseMiddleware))
const asyncAction = dispatch => fetch('/api').then(res =>res.json).then(data => {
dispatch({ type: 'success', payload: { data } })
}).catch(error => {
dispatch({ type: 'failure', payload: { error } })
}))
store.dispatch({ type: 'start' })
store.dispatch(asyncAction())redux-saga,采用 Generator 生成器函数支持异步多 Action
sagas.js 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18import { call, put, takeEvery, takeLatest } from 'redux-saga/effects';
function* asyncAction() {
try {
const data = yield call('/api');
yield put({ type: 'success', payload: { data } });
} catch (error) {
yield put({ type: 'failure', payload: { error } });
}
}
function* mySaga() {
// 支持并发
yield takeEvery('start', asyncAction);
}
function* mySage() {
//不支持并发,前个处理中的相同 type 的 Action 会被取消
yield takeLatest('start', asyncAction);
}
export default mySage;main.js 1
2
3
4
5
6
7import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from 'redux';
import createSagaMiddleware from 'react-saga';
import reducer from './reducer';
import mySaga from './sagas';
const sagaMiddleware = createSagaMiddleware();
conststore = createStore(reducer, applyMiddleware(sagaMiddleware));
sagaMiddleware.run(mySaga);
如何判断项目需要引入 Redux
并非所有应用程序都需要 Redux,是否引入 Redux 由以下决定
- 正在构建的应用程序类型
- 需要解决的问题类型
- 哪些工具可以更好地解决问题
Redux 可以共享和管理状态
- 通过可预测的行为来帮助回答:状态何时、何处、为什么及如何改变
- 增加概念、代码和限制,增加学习成本和项目复杂度
平衡利弊,在以下情况引入 Redux 最有用
- 应用程序许多地方都需要状态
- 应用程序的状态经常更新
- 更新状态的逻辑比较复杂
- 项目较大,需要比较多的人协作
- 想查看状态何时、何处、为什么及如何改变

